What is Trauma?
Trauma is a deeply distressing event that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope.
Examples could include events like:
What is PTSD?




Symptoms of PTSD
Constant reminders of the trauma like memories, nightmares, and flashbacks. Reacting intensely to things that trigger you, or remind you of trauma. These may feel like panic attacks and you may have difficulty calming yourself down. You may also notice it as irritability, easily becoming furious when something reminds you of the trauma.
Avoiding memories, emotions, and things that might remind you of trauma. This can limit the things you do and can include things like using alcohol, drugs, over-working, dissociating, or other unhealthy behaviors to avoid emotions.
Having a more negative outlook in general. Difficulty feeling safe or trusting other people. Poor self-esteem or blaming yourself for what happened. Isolating yourself. Zoning out or feeling disconnected. Feeling sad, guilty, angry, irritable, or numb, and having a hard time feeling good. Individuals may also experience moral injury (the sense that you have betrayed your morals or values) or survivor's guilt (the belief that a bad thing should have happened to you instead of someone else).
Always being on guard or vigilant. Being jumpy or easily startled. Having a hard time managing anger. Trouble focusing and difficulty getting a good night's sleep.
These can manifest in the body, like through headaches, high blood pressure, stomach problems and/or chronic pain.
Trauma & PTSD Services
What is Evidence Based Treatment?
Evidence based treatment means that the therapy has been thoroughly researched and there are data to support that it is helpful. This may mean that there are a set number of sessions, specific things we will cover in session, and skills for you to practice at home. Some therapies may have workbooks or companion apps to support your treatment. We will work with you to make sure the therapy techniques are a good fit for you.
Though much of the research has been conducted in the US, several therapies we offer have been studied in countries across the world and with individuals with marginalized identities. We are also experienced in modifying therapies to fit each person. Feel free to ask us about how a particular approach might work for you.
Types of Trauma & PTSD Therapies
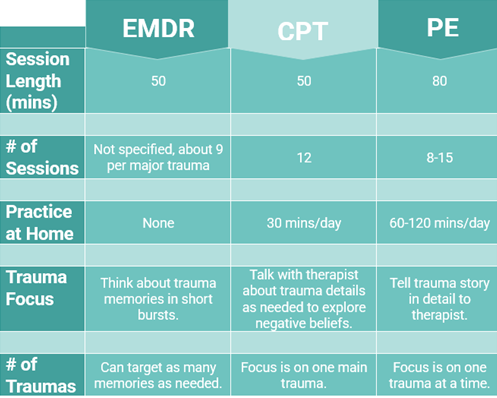
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing Therapy (EMDR) helps individuals approach difficult traumatic experiences so that they can think and feel differently about them. It combines thinking about trauma memories with some type of movement to make it easier. EMDR helps individuals find their own way of making sense of their experiences.
Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT) helps individuals understand how habits in the way they think about their traumas, such as "it was all my fault" or "I have to be on guard all the time," keep them stuck in PTSD. Beliefs about guilt, safety, trust, esteem and intimacy are all addressed. CPT does not require you to retell your trauma stories, but events are talked about as beliefs are examined. Individuals leave CPT with a set of skills they can continue practicing after therapy ends.
Prolonged Exposure (PE) is a therapy that helps individuals begin to face trauma related memories, emotions, and triggers that they have been avoiding. In PE you tell your therapist the story of one of your traumas; this gets easier over time, and you develop a better understanding of the event. Your therapist also helps you identify things PTSD keeps you from doing in your life now, and you make a plan to slowly approach these triggers. Individuals leave PE with a set of strategies they can use to face other traumas and life stressors.
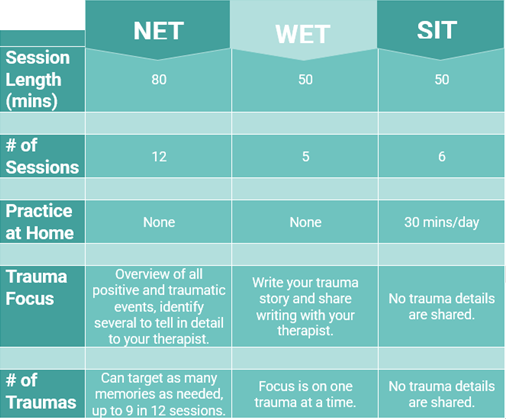
Narrative Exposure Therapy (NET) is a therapy that helps individuals approach their trauma memories by looking at their whole life story. Major life events are identified and individuals choose the most important ones to tell out loud to their therapist. People often find that telling their stories helps them understand how their traumas fit into the larger context of their lives, and they start to think and feel differently about the events. Individuals can leave NET with a collection of all the life stories they shared.
Written Exposure Therapy (WET) is a brief treatment that allows individuals to approach a trauma memory by writing the story of what happened. After you complete your writing in session, your therapist helps you process what you wrote.
Stress Inoculation Training (SIT) is a therapy that helps individuals develop tools for coping with their PTSD symptoms. It explains how PTSD affects the brain, and teaches skills like strategic breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and identifying negative thoughts. These skills can be used when you feel triggered or overwhelmed by traumatic memories. SIT might not reduce your symptoms of PTSD, but it can help you feel more confident in managing them.


Trauma Support
Some individuals may prefer additional support preparing to do an evidence based treatment for PTSD, or want support in continuing to use skills after completing therapy.

It is very common for individuals to develop addictions or substance use disorders as an attempt to cope with their trauma. If you struggle with addiction & trauma, it is best to treat them both together. We can help you decide if an integrated therapy that addresses both at the same time might be best, or if a combination of trauma work and outside recovery support is a better fit. Recovery focused programs like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA/NA) or SMART Recovery can be great supports.
To benefit from trauma treatment, we recommend that you are not under the influence while you are participating in treatment activities, which can mean up to 5 hours of sobriety per day. If this does not feel possible, or would be dangerous for you to try due to withdrawal symptoms, we recommend completing a specialty substance use program before starting trauma treatment.
Trauma treatment might also be offered virtually while you complete residential rehabilitation, if appropriate.
We are stronger together, and family support can be a critical part of recovery from PTSD. We are happy to meet with your loved ones to help them learn more about PTSD and how you can help each other during PTSD treatment.

How do I choose which therapy?
Your therapist will help you review the options so you can choose the one you think is best for you. You can always try a different approach if you find one type of therapy is not a good fit for you.
Sometimes folks might need to try more than one therapy to fully meet their treatment goals, especially if you have experienced more than one type of trauma.
If trauma treatment sounds like too much right now, you might want to consider working on a related issue, like sleep problems.
Research tells us that starting with something simple, like sleep, can help build confidence to engage with trauma treatment later on. Click below to learn more, or contact us to set up a FREE consultation session to discuss options.
Content above is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional assessment or therapy.